Much of a gopher’s feeding and living happens underground in an extensive network of tunnels that serves as its home.
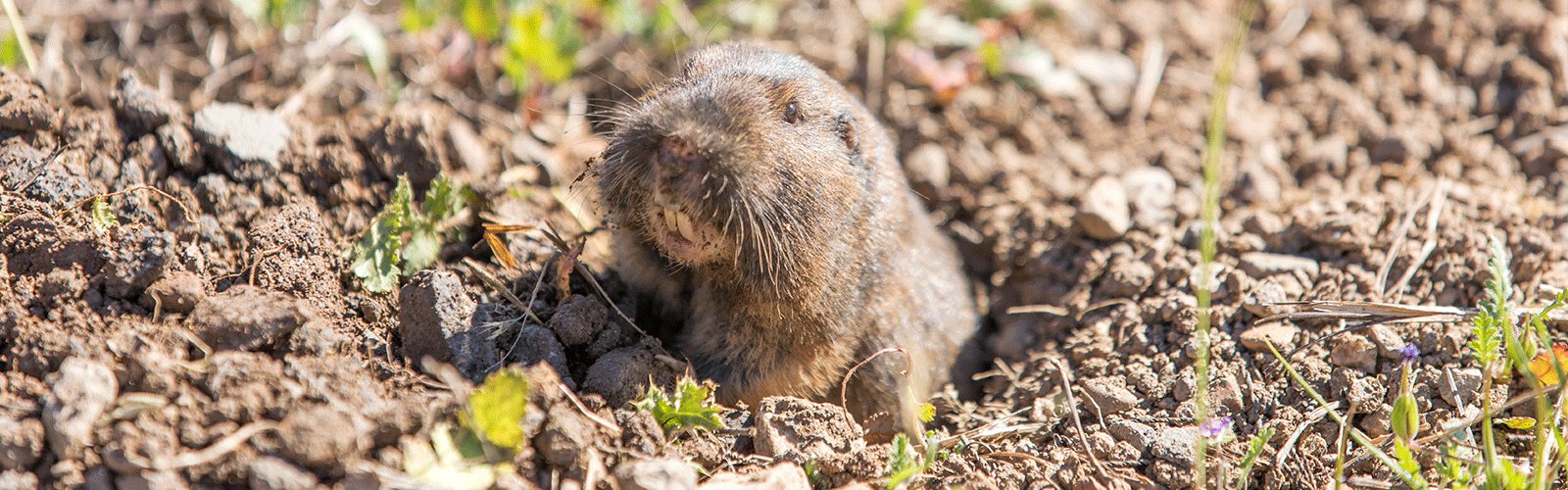
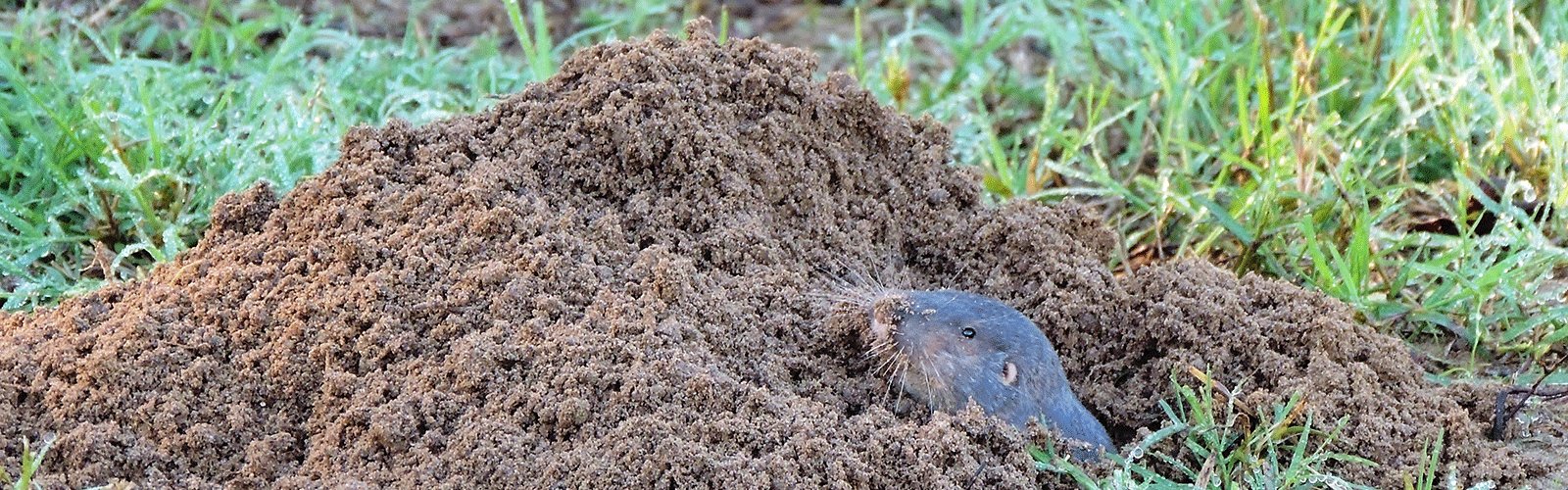
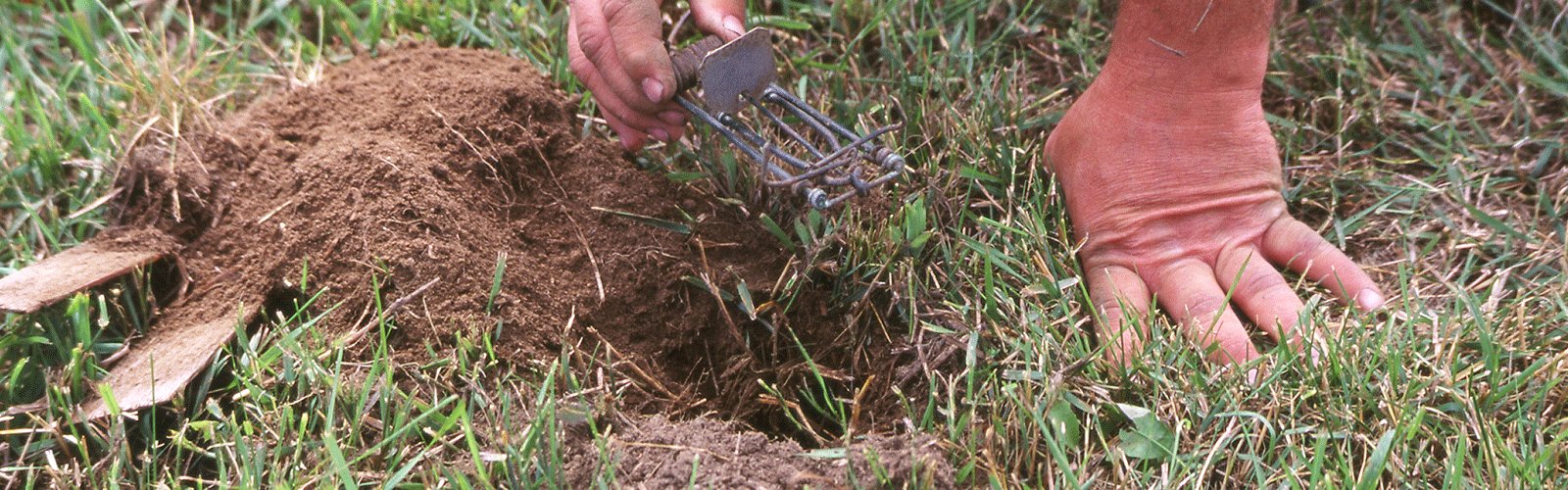
Sometimes called a pocket gopher because of its fur-lined cheek pouches, this small mammal is unique to the Western Hemisphere. Its homelands stretch from Central America to Alberta. This means that much of the U.S. serves as a gopher’s backyard, from coastal areas to high elevations. Unfortunately, its tunnels create a host of problems for North American farmers and homeowners. Along with being part of the food chain, gophers do play an important role in ecology. Their burrowing adds organic matter to soil and increases aeration. But if you think or know that they have caused damage on your property, your first step is to understand gophers and how to spot signs of their activity.